To Perform Penetration Test on Bitumen

(AASHTO DESIGNATION: T-49)
In this test, we examine the consistency of a sample of bitumen by determining the distance in tenths of a millimeter that a standard needle vertically penetrates the bitumen specimen under known conditions of loading, time, and temperature. This is the most widely used method of measuring the consistency of a bituminous material at a given temperature. It is a means of classification rather than a measure of quality.
APPARATUS:
- Penetration Apparatus
- Needle
- Container
- Water Bath
- Thermometer for Water Bath
- Stopwatch
Principle:
It measures the hardness or softness of bitumen by measuring the depth in tenths of a millimeter to which a standard loaded needle will penetrate vertically in 5 seconds.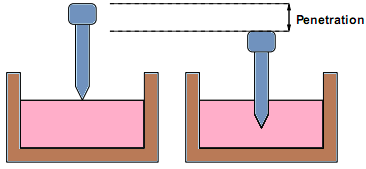
PROCEDURE:
- Heat the sample until it becomes fluid.
- Pour it into a container to a depth such that when cooled, the depth of the sample is at least 10mm greater than the expected penetration.
- Allow it to cool at an atmospheric temperature.
- Clean the needle and place a weight above the needle.
- Use the water bath to maintain the temperature of the specimen.
- Mount the needle on the bitumen, such that it should just touch the surface of the bitumen.
- Then start the stopwatch and allow the penetration needle to penetrate freely at the same time for 5 seconds. After 5 seconds stop the penetration.
- The result will be the grade of bitumen.
- Take at least three readings.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Bitumen Penetration Test
Sample Preparation:
Obtain a representative sample of bitumen, ensuring that it is homogeneous and free from any contaminants. The sample should be at a specified temperature for testing, typically around 25 degrees Celsius.
Penetration Apparatus Setup:
Set up the penetration apparatus, which consists of a penetrometer, a needle, and a penetration measurement gauge. The penetrometer usually consists of a vertical rod with a calibrated dial gauge or digital display.
Conditioning:
If required, condition the bitumen sample at the specified temperature to ensure consistency in the test conditions. Conditioning may involve heating or cooling the sample to achieve the desired testing temperature.
Test Procedure:
Place the prepared sample in a penetration cup or container. The penetration needle, typically made of stainless steel, is positioned vertically above the sample.
Needle Placement:
Lower the needle gently onto the surface of the bitumen sample, ensuring it makes contact without applying any additional pressure. Allow a few seconds for the needle to settle before proceeding.
Test Initiation:
Release the needle from its rest position and allow it to penetrate the bitumen sample under its own weight. The penetration is usually timed for a specific duration, typically 5 seconds.
Recording Penetration Value:
After the specified time, record the depth of penetration in tenths of a millimeter. The penetration is measured as the distance the needle has traveled vertically into the bitumen sample.
Repetition:
Repeat the test with the same sample at least two more times to ensure the accuracy and consistency of results. If there is a significant difference in penetration values, conduct additional tests and calculate the average.
Cleaning:
Clean the penetration needle and the penetration cup thoroughly between tests to avoid any cross-contamination and to maintain accurate results.
The penetration value obtained from the test represents the consistency or hardness of the bitumen. It helps classify different grades of bitumen based on their penetration values and assists in determining their suitability for specific applications.
Note: The specific procedure and equipment used for the penetration test may vary slightly depending on the applicable standards or specifications being followed. It is essential to refer to the appropriate standards or guidelines for the exact details of the test procedure
USES AND SIGNIFICANCE:
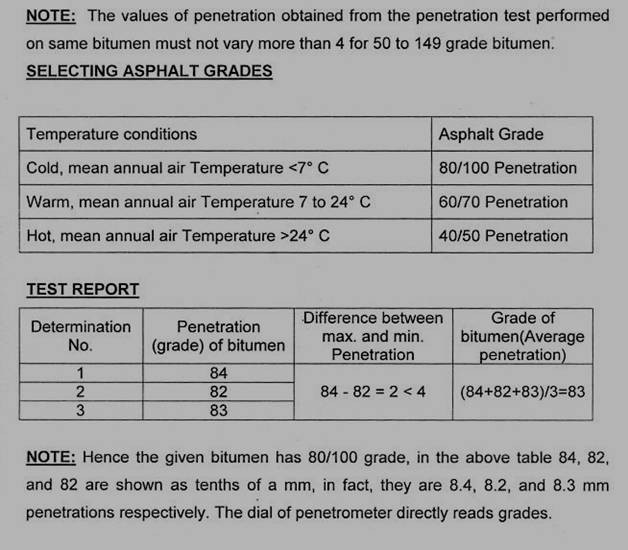
A penetration test is used to measure the consistency of bitumen so that it can be classified into standard grades. A greater value of penetration indicates softer consistency. Generally higher penetration bitumen is preferred for use in cold climates and smaller penetration bitumen is used in hot climate areas.
- It measures the hardness or softness of bitumen by measuring the depth in tenths of a millimeter to which a standard loaded needle will penetrate vertically in 5 seconds
- The penetrometer consists of a needle assembly with a total weight of 100g and a device for releasing and locking in any position
- The bitumen is softened to a pouring consistency, stirred thoroughly, and poured into containers at a depth of at least 15 mm in excess of the expected penetration.
- The test should be conducted at a specified temperature of 25 °C
- It may be noted that penetration value is largely influenced by any inaccuracy with regard to the size of the needle, the weight placed on the needle, and the test temperature
- A grade of 40/50 bitumen means the penetration value is in the range of 40 to 50 at standard test conditions
- In hot climates, a lower penetration grade is preferred.
Grading of the Bitumen on the Basis of Test Results